Viscosity Of Air 25c
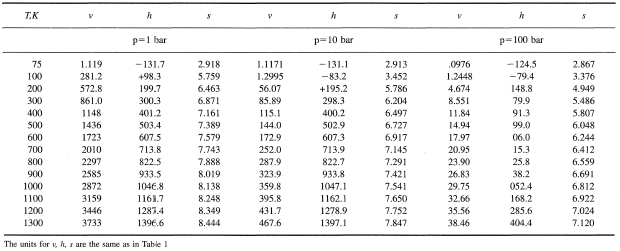
Formulas for ViscosityA widely used formula for the calculation of viscosity of gases is the Sutherland Equation given bywhere b and S are constants and T is temperature expressed in Eq. 1.8 .For air and . Power Law is another approximation to calculate viscosity and isgiven by
where is the value of viscosity at a reference temperature ,which could be 273K. An empirical fit for the viscosity of liquids is For water, = 273.16K, = 0.001792 kg/(m.s), a=-1.94,b = -4.80 and c = 6.74. Another empirical formula for liquids is the Andradeequation namely,
where and are constants and is the temperature in K (c) Aerospace, Mechanical & Mechatronic Engg. 2005University of Sydney |
Viscosity Charts & Conversion Tables DAIRY PRODUCTS ButterFat 42 110 ButterFat 20 150 ButterDeodorized 45 120 CottageCheese 30,000 65 CocoaButter 50 140 CocoaButter 0.5 210 CondensedMilk 40–80 100–120 CondensedMilk,75%Solids 2,160 70 Cream,30%Fat 14 60 Cream,45%Fat 48 60 Cream,50%Fat 112 60 Cream,50%Fat 55 90 Milk 2.0 65 Milk 10 120.
Viscosity Of Air At 20 C
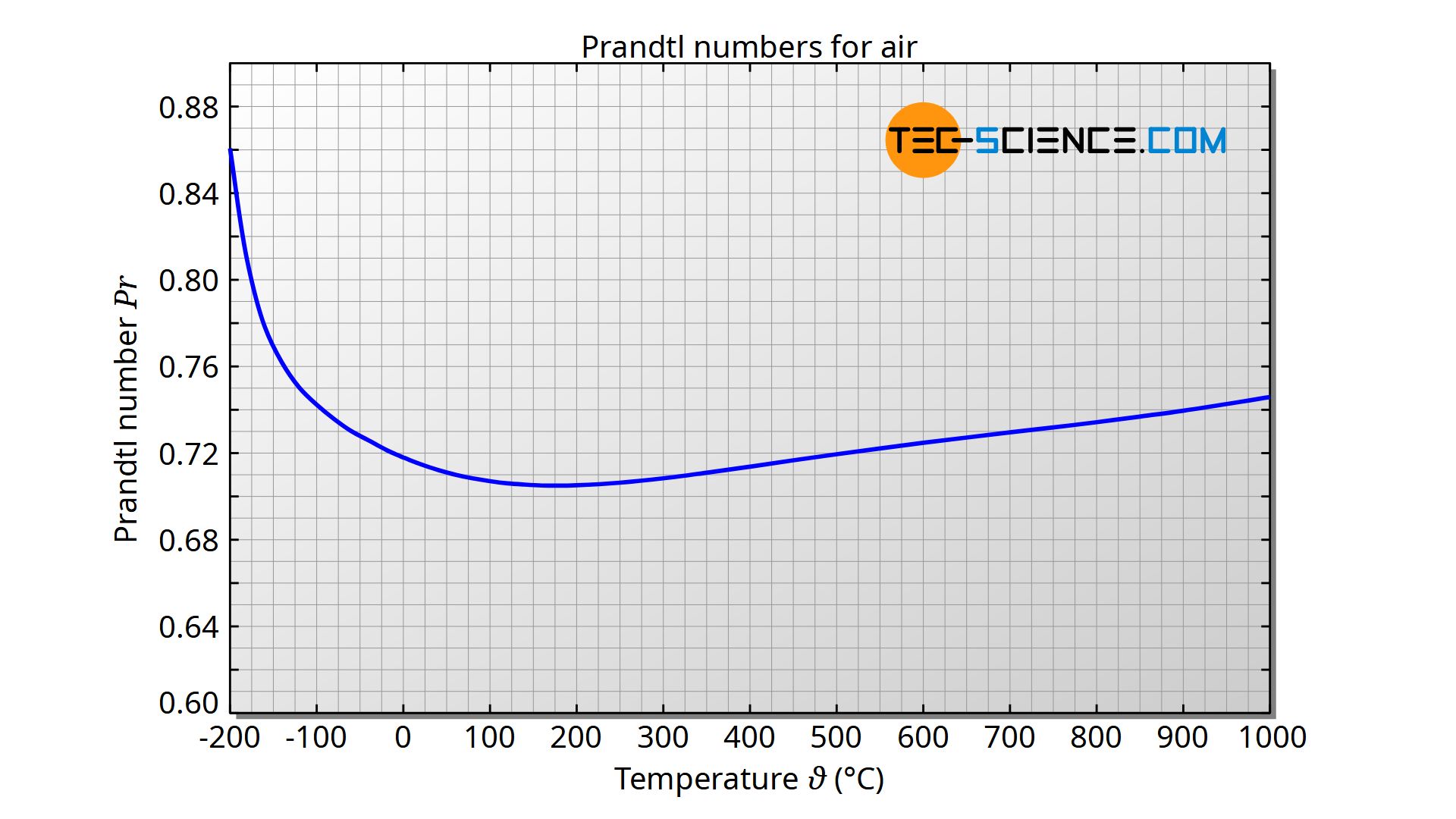
- The kinematic viscosity n (SI units m2/s) is, by definition n ¼ m r The Prandtl number is, by definition, Pr ¼ c Pm k For consistency this may be found by substitution. A direct empirical expression in the case of air is Pr ¼ 0:680 þ4:69 10 7ðT K 540Þ2 In practice, for normal air cooling Pr 0:70 Properties of Air 377.
- As a result, molecules start colliding with each other at a faster rate, and hence, the viscosity of air, i.e., increases with the temperature rise. Question 4: State Density Versus Viscosity. Answer: We define density as the measurement of the molecular weight of the molecules of gas/liquid/fluid.
- The viscosity of air, at atmospheric pressure is the following: Air viscosity at 0°c = 0.01722 mPa.s Air viscosity at 25°c = 0.0186 mPa.s 2.